![What Is Yoga? Which means, Philosophy, Historical past, and Advantages Defined [With Infographics] – Fitsri Yoga What Is Yoga? Which means, Philosophy, Historical past, and Advantages Defined [With Infographics] – Fitsri Yoga](https://fitsri.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/07/what-is-yoga-brief-info.jpg)
Whenever you first hear the phrase yoga, you would possibly image bodily postures or respiratory workouts. Many individuals suppose yoga is only a means to enhance flexibility, construct energy, or calm down the thoughts.
However yoga is far more than that. It’s a path that connects the physique, thoughts, and soul. It helps you uncover your true self and reside with better consciousness.
On this article, we discover the conventional Indian that means of yoga, its historic roots, and the way it has unfold the world over. From its origin to its deeper objective, right here is the whole lot you’ll want to learn about what yoga actually is.
Definition of yoga
Yoga is a lifestyle that helps an individual attain their highest potential. It’s the path that results in interior consciousness and unity with your entire creation.
The phrase yoga comes from the Sanskrit root ‘Yuj’, which implies to hitch or to unite. Yoga is the observe of making connection at each degree of being.
By way of yoga, we join:
- The soul with the supreme soul
- The ego-self with the upper Self
- Particular person consciousness with common consciousness
- The physique and thoughts with the soul
This union is the true objective of yoga. It goes past bodily train and turns into a journey of self-realisation.

3 Points of Yoga
Yoga is historically practised by three core elements self-discipline, devotion, and information. Collectively, these information the yogi in the direction of Samadhi, the state of full religious absorption.
Though totally different religions have formed their very own objectives for yoga, the fundamental construction and sequence of observe stay constant throughout traditions.
Yoga originated in India and has all the time included a mixture of practices that assist bodily, psychological, and religious development. These embody:
- Residing by ethical and moral values
- Finding out religious philosophy
- Practising bodily postures (asanas) to maintain the physique sturdy and versatile
- Utilizing respiratory strategies (pranayama) to regulate the life power (prana)
- Chanting mantras to focus the thoughts and uplift power
- Meditating to quiet the thoughts and join with the interior self
Historical Hindu sages and ascetics adopted this path with deep dedication. By way of common and disciplined observe, they skilled a union of physique and thoughts with the supreme soul, also referred to as pure consciousness. On this deep meditative state, the mind (buddhi) turns into nonetheless and silent.
This state is known as Ananda, that means interior bliss. It’s the expertise of peace past the distractions of the fabric world, the place one feels full oneness with the universe.
Within the fashionable world, yoga is usually considered as a bodily exercise or a leisure methodology. Nevertheless, at its core, yoga is a religious science that results in self-realisation.
From the very starting, the true purpose of yoga has been to information every individual in the direction of their actual naturebeyond physique and thoughts.
Even fashionable science helps this concept, suggesting that your entire universe is fashioned from a single supply of refined power. An individual who turns into one with this power is claimed to be within the state of yoga.
The science of yoga: how does it work?

The science of yoga is deeply rooted in historic knowledge and was systematised by sage Patanjali, an ideal Indian thinker and psychologist from the 2nd century BCE. He compiled the foundational textual content of classical yoga, often known as the Yoga Sutra, and is usually referred to as the father of classical yoga.
Patanjali’s Yoga Sutra focuses on mastering the thoughts, rising spiritually, and studying to understand past the 5 bodily senses.
He understood that most individuals rely upon the surface world for fulfilment. This fixed seek for exterior success creates patterns of thought within the thoughts, resulting in restlessness and distraction. Because of this, our consciousness turns outward, and we neglect to ask deeper questions like:
- Who am I?
- Why am I right here?
- What’s the reality of my existence?
Yoga helps us return to those questions by calming the thoughts and balancing the physique.
How does yoga calm the thoughts?
After we practise a yoga pose, a respiratory approach, or meditation, we direct our consideration to a selected motion or feeling. This targeted consciousness permits the thoughts and physique to work collectively.
As this connection grows stronger, we cease relying solely on the restricted info offered by our senses. The physique and thoughts start to stabilise.
When this interior stability is achieved, our consciousness turns inward, and the fixed stream of ideas slows down. That is how yoga helps cut back psychological noise and brings readability and stillness.
By way of constant observe, yoga permits us to maneuver past psychological distractions and expertise the deeper self inside.
Basis of yoga: yogic philosophy
The philosophy of yoga is among the six main faculties of Indian philosophy, often known as the Shad Darshanas. These are:
Samkhya, Yoga, Nyaya, Vaisheshika, Mimamsa, and Vedanta.
Amongst these, Yoga philosophy is essentially the most sensible. It combines religious information with step-by-step strategies for private transformation. Whereas Samkhya is a non-theistic path to liberation (moksha), Yoga contains the thought of surrendering to a better energy, referred to as Ishvara (God), as a part of the trail to liberation.
Core Ideas of Yogic Philosophy
Yoga philosophy relies on 5 primary ideas:
- Purusha and Prakriti – the 2 basic components of existence
- Trigunas – the three qualities of nature that affect the thoughts and behavior
- Yamas and Niyamas – moral ideas for a disciplined life
- Ashtanga Yoga – the eight-limbed path described by Patanjali
- Paths of Yoga – 4 religious paths to self-realisation
1. Purusha & Prakriti
In accordance with yoga philosophy, our existence has two layers:
- Prakriti (nature or matter) – permits us to expertise the bodily world
- Purusha (pure consciousness or soul) – is the true self, the silent observer
Purusha is everlasting, changeless, and free from ache or want. It’s the supply of all expertise however stays unaffected by it.
Prakriti, then again, is the ever-changing materials world. It contains the physique, thoughts, senses, and feelings. It’s by Prakriti that we reside and act, however it is usually what creates illusions (Maya) that maintain us connected to worldly issues.
Yoga teaches that the soul (Purusha) sees the world by filters or impressions created by the thoughts. These psychological patterns are often known as Vrittis, as described in Patanjali’s Yoga Sutra:
“Yoga Chitta Vritti Nirodha” – Yoga is the stilling of the fluctuations of the thoughts.
After we cease figuring out with the thoughts and its patterns, we reconnect with our true self. The observe of yoga helps dissolve these Vrittis and frees us from the phantasm created by Prakriti.
2. Tri-Gunas
Trigunas are the three qualities that make up human nature and affect the way in which we expect, really feel, and act:
Sattva, Rajas & Tamas are the three qualities of a residing being.
- Sattva – purity, readability, knowledge, peace
- Rajas – power, ardour, motion, want
- Tamas – darkness, laziness, ignorance, confusion
Each particular person carries a mixture of these three qualities, however one is normally dominant at a time. The objective of yoga is to extend Sattva, which results in readability of thoughts, stability, and religious development.
By lowering Rajas and Tamas by moral residing, aware actions, and meditation, we transfer in the direction of a extra peaceable and conscious state of being.
Historical past of yoga: origin & improvement timeline
The historical past of yoga goes again 1000’s of years. It developed by varied levels, every contributing to how we perceive and practise yoga as we speak. Here’s a timeline of the foremost intervals within the historical past of yoga:
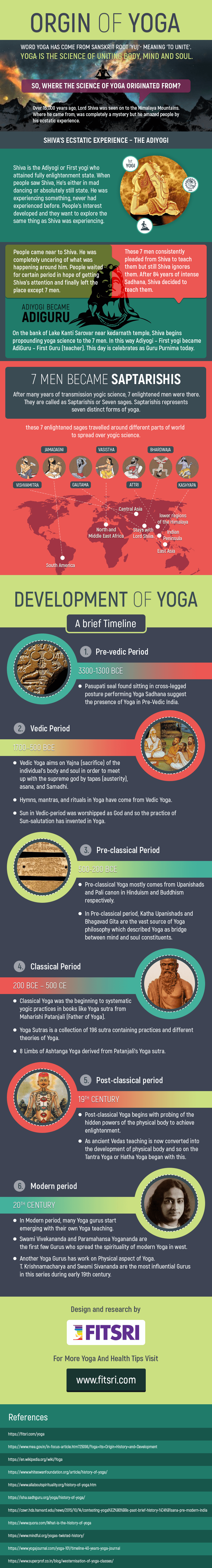
1. Pre-vedic interval (3300–1300 BCE)
Indicators of early yoga practices had been discovered within the Indus–Saraswati Valley Civilisation in Northern India. Seals from this time present figures in meditative postures, suggesting the roots of yoga had been already forming.
2. Vedic interval (1700–500 BCE)
The Vedas are the oldest sacred texts of Hinduism, containing hymns, mantras, and rituals. The phrase “Yoga” was first talked about within the Rigveda.
The Atharvaveda describes a gaggle of ascetics referred to as Vratyas who practised bodily postures that later developed into fashionable yoga poses.
Throughout this time, Rishis or Vedic yogis shared religious teachings and guided folks in rituals, meditation, and Tapas (austerity). This is named Vedic Yoga, geared toward uniting with the divine by self-sacrifice and deep meditation..
3. Pre-classical interval (500–200 BCE)
On this interval, yoga concepts started showing in religious texts just like the Upanishads and the Bhagavad Gita.
The Katha Upanishad described yoga as a bridge between the thoughts and the soul, achieved by posture, breath management, and targeted meditation.
The Bhagavad Gita launched three primary paths of yoga:
In Buddhism, early texts just like the Pali Canon additionally described meditation and mindfulness practices much like yogic teachings.).
4. Classical interval (200 BCE – 500 CE)
This era noticed the event of a transparent and organised system of yoga, primarily by the work of sage Patanjali.
Patanjali compiled the Yoga Sutras, a set of 196 aphorisms that laid the inspiration of Classical Yoga or Raja Yoga the yoga of controlling the thoughts.
The Ashtanga Yoga system (Eight Limbs of Yoga) described in these sutras contains moral guidelines, postures, breath management, and meditation, all geared toward reaching Samadhi (religious liberation).
5. Publish-classical Interval
This era shifted the main target of yoga from liberation alone to enhancing life within the current second.
Texts just like the Bhagavata Purana launched Viraha Yoga practices of separation from the fabric world to attach with Krishna by devotion and meditation.
Later, yoga masters explored the physique’s hidden power programs. This led to the rise of Tantra Yoga, which mixes breath, motion, sound, and rituals to awaken larger consciousness.
6. Trendy interval (18th century – current)
The fashionable period introduced yoga to the worldwide stage.
Swami Vivekananda was one of many first Indian yogis to unfold yoga within the West. His speech on the Parliament of the World’s Religions in Chicago in 1893 launched the religious depth of yoga to a worldwide viewers.
Different key figures embody:
- Paramahansa Yogananda, who launched Kriya Yoga and based the Self-Realization Fellowship
- Swami Sivananda, who established the Divine Life Society in Rishikesh and authored over 200 books on yoga philosophy and observe
Within the twentieth century, Hatha Yoga turned standard within the West by the efforts of recent yoga masters like:
- T. Krishnamacharya – thought of the daddy of recent yoga, opened a yoga college in Mysore in 1931
- B.Ok.S. Iyengar – founding father of Iyengar Yoga, identified for exact alignment and using props
- Pattabhi Jois – developer of Ashtanga Vinyasa Yoga
- T.Ok.V. Desikachar – founding father of Krishnamacharya Yoga Mandiram (KYM), a centre for yoga remedy in Chennai
These lecturers helped remodel yoga right into a worldwide observe, combining conventional knowledge with fashionable wants.
The yogic tree: 6 primary branches of yoga
Yoga shouldn’t be restricted to bodily workouts. It’s a full science of life that helps stability physique, thoughts, and soul. Historical yogis developed six primary branches of yoga to information folks with totally different pursuits and temperaments towards one widespread objective Self-realisation.
Every department has its personal path and methodology, however all purpose to carry interior peace and union with the upper self. You’ll be able to practise one or a mixture of branches primarily based in your nature and life objectives.
1. Hatha Yoga
Hatha Yoga is essentially the most well-known department as we speak and types the bottom of recent yoga. The phrase “Hatha” comes from “Ha” (solar) and “Tha” (moon), symbolising the stability of energies throughout the physique.
It focuses on:
- Bodily postures (asanas)
- Respiration strategies (pranayama)
- Purification and interior stability
Hatha Yoga prepares the physique for deeper religious practices by making it sturdy, secure, and calm.
2. Tantra Yoga
Tantra Yoga is a religious science that makes use of rituals, breath, sound, and motion to awaken refined energies within the physique. It goals to beat the restrictions of physique and thoughts attributable to repetitive patterns and attachments.
Key practices embody:
Tantra is usually misunderstood however at its core, it helps develop consciousness and religious consciousness.
3. Karma Yoga
Karma yoga is the pathway to selfless motion. In accordance with karma philosophy, each motion is served as an providing to the divine (God) with none end result desired. Karma yoga is one thing you’ll be able to observe out of mat anytime, anyplace.
To study extra about what advantages karma yoga offers when practiced repeatedly, it’s best to positively learn this information of karma yoga.
4. Bhakti Yoga
Bhakti Yoga is the trail of affection, devotion, and give up to a better energy or deity. It entails heartfelt prayer, chanting, and seeing the divine in all beings.
Practices embody:
- Singing devotional songs (bhajans or kirtans)
- Prayer and worship
- Providing each thought and motion to God
Bhakti Yoga softens the guts, removes ego, and results in deep emotional reference to the divine.
5. Jnana yoga
Jnana Yoga is the yoga of interior knowledge. It helps you uncover the reality by asking questions like “Who am I?” and “What’s actual?”
Foremost instruments of Jnana Yoga:
- Self-inquiry (atma vichara)
- Research of religious texts (like Upanishads and Bhagavad Gita)
- Reflection and meditation
It’s best suited to seekers with a pointy mind and a deep curiosity in religious information.
6. Raja Yoga
Raja Yoga, also referred to as the “Royal Path“, focuses on gaining management over the thoughts. It’s primarily based on the Yoga Sutras of Patanjali, which describe the eight-limbed path (Ashtanga Yoga).
These steps embody:
Raja Yoga is an entire path for mastering ideas, feelings, and consciousness.
Yoga Advantages
Folks usually search for a purpose earlier than beginning one thing new. Within the case of yoga, there usually are not only one or two, however dozens of confirmed advantages on your physique, thoughts, and soul.
Yoga works on each degree of your being—from tiny cells to main organs. It helps bodily well being, psychological readability, emotional stability, and religious development.
Listed here are some key advantages of practising yoga repeatedly:
- Improves flexibility and energy
- Helps wholesome posture and backbone alignment
- Enhances focus, reminiscence, and psychological calmness
- Reduces stress, anxiousness, and melancholy
- Improves digestion, metabolism, and immunity
- Promotes higher sleep and power ranges
- Balances hormones and boosts circulation
- Will increase self-awareness and mindfulness
- Helps in emotional therapeutic and self-acceptance
- Connects you with interior peace and readability
Whether or not you wish to enhance your well being, cut back stress, or discover your religious path, yoga gives an entire system to assist your journey.
👉 Discover 46 Science-Backed Advantages of Yoga
Conclusion
Yoga isn’t just train it’s a lifestyle. Rooted in historic Indian knowledge, it continues to information folks the world over in the direction of well being, concord, and self-awareness.
Whether or not you search higher bodily well being, a relaxed thoughts, or religious development, yoga gives an entire path to remodel your life.