A groundbreaking dataset charts the distribution of kissing bug species throughout three continents, offering public well being officers with the insights wanted to stop new Chagas illness outbreaks.
Information launch: Triatomines outdoors the Americas: a complete dataset for the worldwide surveillance of Chagas illness vectors. Picture Credit score: Oktavianus Mulyadi / Shutterstock
In a current examine revealed within the journal Gigabyte, researchers investigated, collated, and synthesized the primary complete dataset monitoring the worldwide distribution of non-American populations of 16 species of “kissing bugs” (triatomine bugs), the uncared for vectors of Chagas illness.
The compiled useful resource particulars the places of those bugs throughout Africa, Asia, and Oceania, primarily based on practically a century of information, offering a essential device for worldwide surveillance and serving to public well being officers assess and handle the danger of native Chagas transmission worldwide.
Background
Chagas illness (“American trypanosomiasis”) is a tropical parasitic sickness attributable to the Trypanosoma cruzi parasite, characterised by delicate, flu-like, or unnoticeable signs (acute section) adopted by doubtlessly deadly injury to the guts and digestive system (continual section) years later.
Historically restricted to Latin America, the worldwide dispersal of the parasite by means of anthropogenic switch (human migration) is elevating substantial issues about potential international outbreaks throughout nearly each continent. Chagas illness is primarily transmitted by means of contact with the feces of contaminated bugs generally known as triatomine bugs, which purchase the parasite by biting an contaminated human.
International outbreak fears centre across the following situation: if an contaminated individual settles in a area the place native kissing bugs exist, these native bugs might chew the affected person, develop into contaminated themselves, and set up a brand-new cycle of transmission removed from the illness’s native American origin.
Sadly, whereas enhanced surveillance could have prevented native illness outbreaks, a persistent lack of a transparent, consolidated map of the place these potential vectors exist in Africa, Asia, and Oceania has hampered vector monitoring efforts.
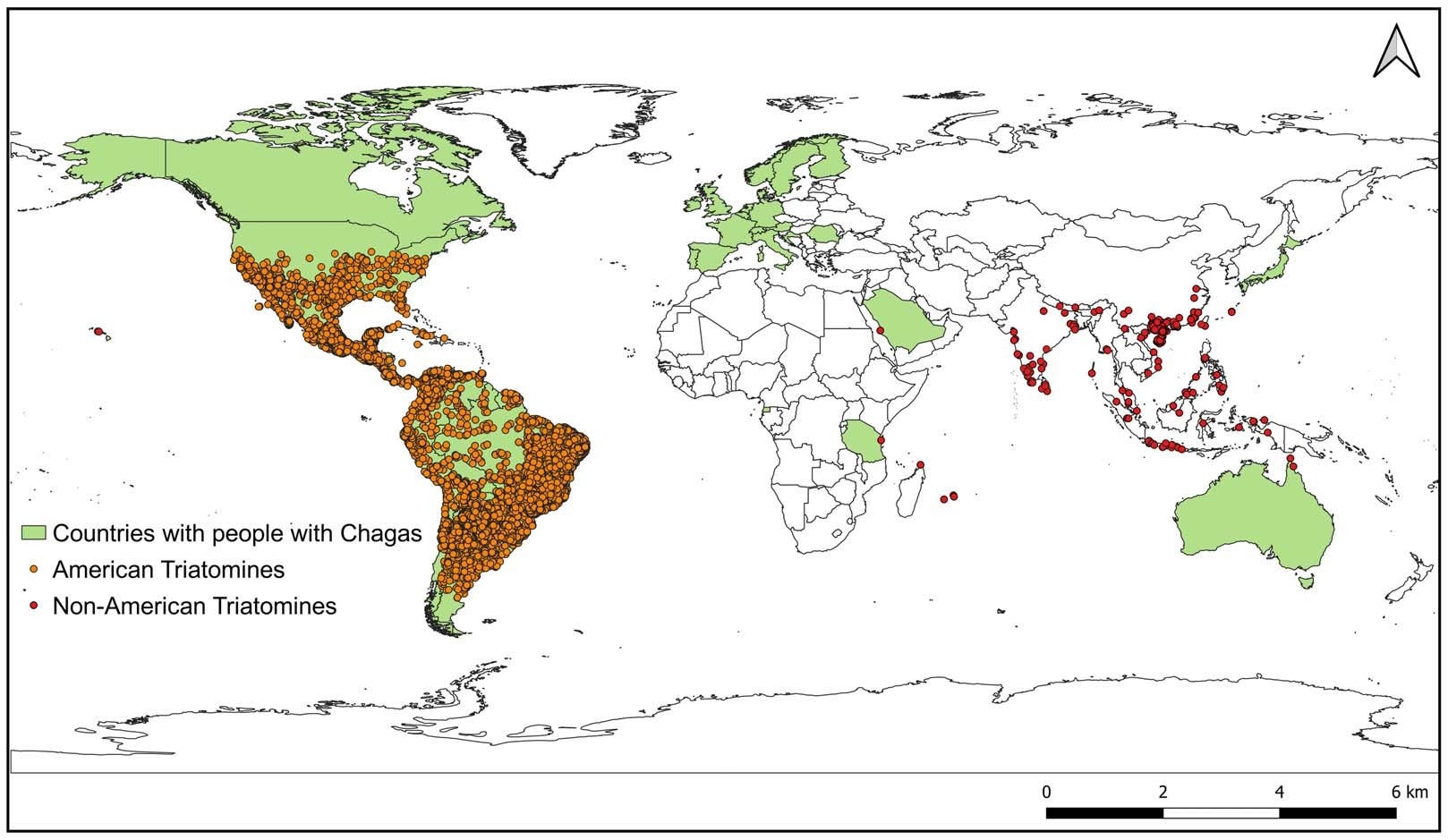
International distribution of individuals with Chagas illness and triatomine vectors. Inexperienced polygons point out international locations with individuals contaminated with Trypanosoma cruzi, in keeping with the newest official estimates (2018). Orange dots symbolize information of American triatomine speciesand pink dots symbolize non-American triatomine species
Concerning the Research
The current examine goals to handle this data hole and inform public well being efforts by consolidating practically a century of sightings of 16 species from the genera Triatoma and Linshcosteus outdoors their native American vary.
The dataset comprised information collected between 1926 and 2022, acquired from scientific publications, museum collections, and public biodiversity databases (n = 7: BioOne, PLoS, Google Scholar, ScienceDirect, Wiley, PubMed, and Scielo), in addition to citizen-science platforms corresponding to iNaturalist/GBIF. The dataset additional integrated unpublished knowledge from collaborators, offering essentially the most up-to-date data doable.
All information had been subjected to a rigorous and meticulous screening and verification course of, with all included datapoints cleaned for errors and georeferenced utilizing Google Earth (assigned exact geographic latitude and longitude coordinates). Darwin Core phrases had been leveraged to collate and synthesize per-sample metadata (n = 6), together with specimen identifiers, systematic data, geographical data, temporal data, sampling notes, and particular person particulars.
Research Findings
The current work’s remaining product (novel database) is a sturdy and open-access dataset containing 396 verified information for 16 totally different species of kissing bugs. It gives essentially the most correct map thus far of those potential Chagas vectors throughout 34 international locations and abroad territories in Africa, Asia, and Oceania.
Probably essentially the most important examine discovering issues Triatoma rubrofasciata, a extremely adaptable generalist species that accounts for 317 of the 396 included information. Traditionally related to coastal port cities (probably because of anthropogenic transport by way of ships), the examine reveals that this bug has established populations lots of of kilometers inland in international locations corresponding to China, India, and Vietnam, vastly increasing its recognized territory and potential to transmit Chagas illness.
The current examine additionally consists of the first-ever public geographical information for 2 newly described species, Triatoma atrata and Triatoma picta, each of which happen in China. For a lot of different species, the current dataset gives the primary scientific affirmation of species presence in a specific area in additional than 50 years, changing obscure historic notes with concrete, verified, and trendy proof.
Notably, regardless of the dataset spanning 1926 by means of 2022, over 95% of the information for the widespread T. rubrofasciata have been collected in simply the final 10 years, highlighting the facility of recent knowledge assortment and the alarming, human-mediated unfold of this Chagas illness vector.
The authors additionally emphasize that about 27% of the information lacked assortment dates, round 7% lacked geographic coordinates, and most information got here from domiciliary or peridomiciliary habitats, highlighting potential knowledge biases that must be thought of in future analyses.
They additional word {that a} historic file of T. rubrofasciata from Spain was excluded because of unsure geographic data, highlighting the danger of passive transport and the necessity for cautious validation.
Conclusions
The current examine gives the primary complete catalogue of non-American kissing bugs, providing public well being officers and authorities businesses the knowledge essential to carry out correct danger assessments and design focused vector management methods. It enhances present American and Argentinean triatomine datasets as a part of an built-in international surveillance framework.
As Chagas illness continues its silent unfold throughout continents, figuring out the place its vectors stay is the primary and most crucial step in stopping new, localized outbreaks.
Journal reference:
- Ceccarelli, S., Vicente, M. E., Liu, Q., Zhou, X.-N., Wu, D., Balsalobre, A., Bruno, E. A., Barboza, S. E., Valente, R., & Marti, G. A. (2025). Triatomines outdoors the Americas: a complete dataset for the worldwide surveillance of Chagas illness vectors. Gigabyte, 2025. DOI – 10.46471/gigabyte.163, https://gigabytejournal.com/articles/163